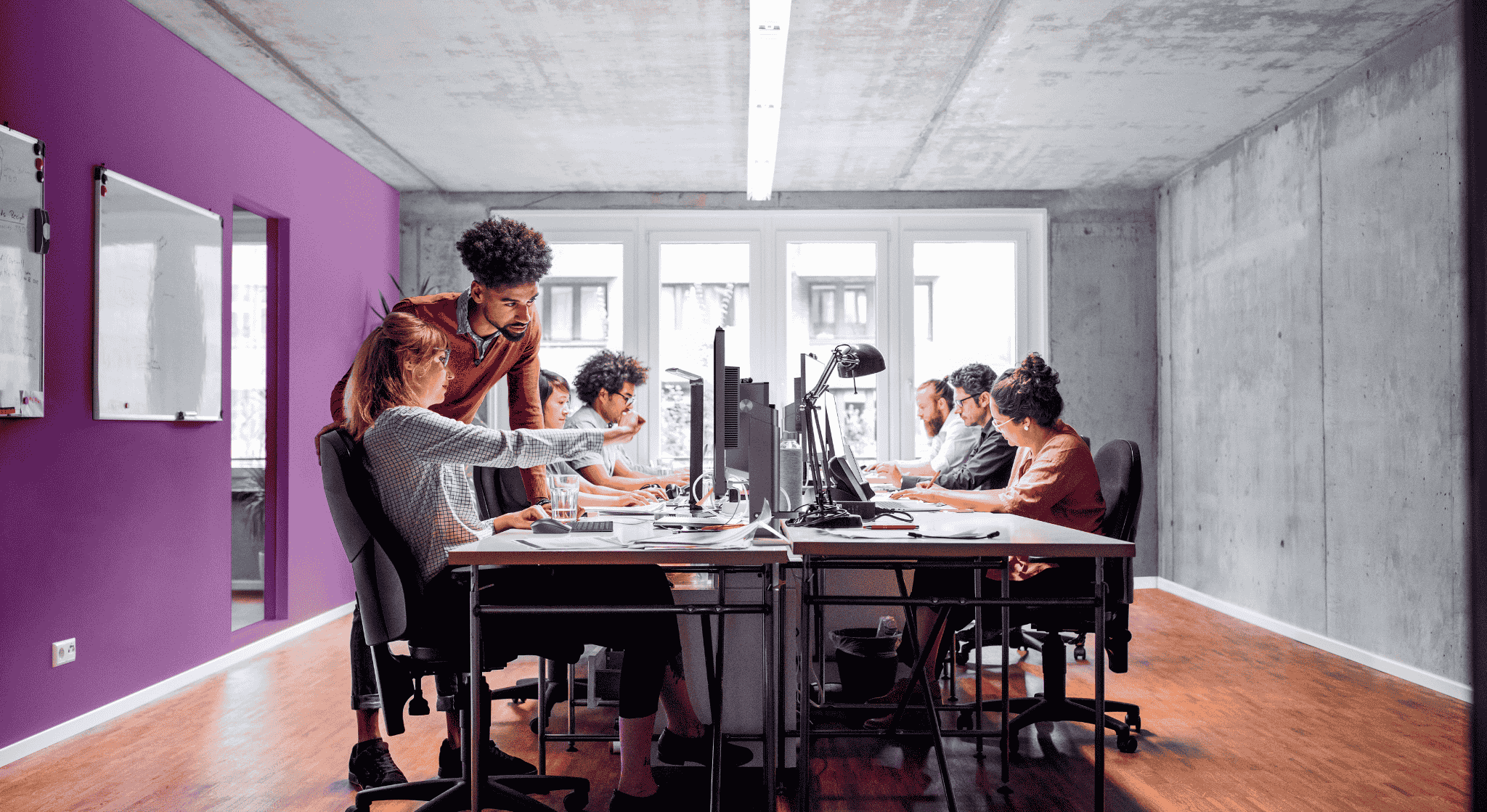
In today's complex threat landscape, security is no longer an optional add-on but rather a fundamental requirement for businesses of all sizes. Lenovo's ThinkShield security platform addresses these needs with a multi-layered approach, providing robust protection from the supply chain to the cloud. This article will explore the key components of Lenovo ThinkShield, its benefits, and how it compares to the competition, HP.
Lenovo's ThinkShield security framework employs a multi-layered approach to safeguard devices throughout their lifecycle. The foundation rests on a Zero Trust Supply Chain, prioritizing the integrity of devices from their inception. This layer ensures that hardware components are genuine and free from tampering during manufacturing. Building upon this, the Below the OS layer focuses on firmware-level protection, encompassing critical components like the BIOS and enabling secure remote management capabilities. Finally, the OS-to-Cloud layer addresses specific security needs and provides comprehensive endpoint protection by integrating with various operating systems and cloud-based security services. This layered approach offers a robust defense against evolving threats by addressing security vulnerabilities at multiple levels, from the hardware to the cloud.
Zero Trust Supply Chain: Securing the Foundation
Zero Trust is a pivotal strategy in today's dynamic business landscape, particularly for mobile and remote workforces. As organizations increasingly rely on "systems of engagement" to connect with customers and suppliers and embrace cloud-centric IT delivery models, Zero Trust becomes crucial for achieving agility. However, the impact of cybersecurity extends beyond mere agility. Effective cybersecurity fosters rapid innovation and expedites market entry by enabling the secure utilization of data for critical insights without escalating business and compliance risks. Furthermore, robust cyber resilience is paramount for building resilient supply chains. This mitigates the impact of erratic pricing, delivery disruptions, and other vulnerabilities that can erode customer relationships, damage market share, and even threaten the viability of SMBs and midmarket businesses.
While Zero Trust provides a foundational framework for secure operations, its effectiveness hinges on the security of the individual devices that access and interact within this framework. Recognizing this, Lenovo prioritizes device security from its very inception. The foundation of this approach lies in its robust supply chain security, centered around the Trusted Supplier Program. This program involves a rigorous vetting and validation process for all partners and suppliers, ensuring the integrity of components even before they are integrated into Lenovo devices. A key component of this layer is "Build Assure," a unique offering that provides a comprehensive view of the components within a device at the point of manufacturing, further enhancing transparency and control over the device's security posture.
- Encrypted Snapshots: Build Assure takes an encrypted snapshot of the critical components within a device during manufacturing. The IT team can then use this snapshot to validate that the components are legitimate and have not been tampered with during the manufacturing or logistics process.
- Runtime Attestation: Lenovo has enhanced this offering to include runtime attestation. This allows IT teams to verify the integrity of device components not just at the point of delivery but also at any point after the device has been deployed. This feature is particularly valuable in today's hybrid and remote work environments, where devices can be exposed to various risks.
- Verification of Components: IT managers can confirm that all components are legitimate and have not been tampered with. This offers supply chain security and provides governance by verifying that components are correctly sourced.